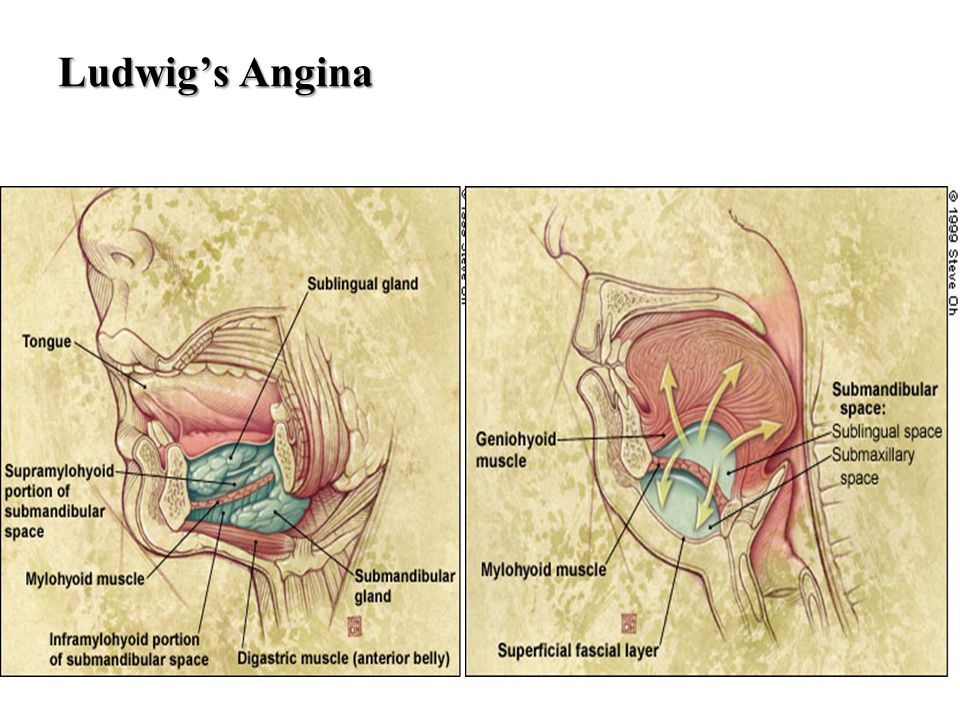
Review the pathophysiology of Ludwigs angina. More specifically it is a bilateral infection of the submandibular space.

Pin De Dr Abuaiad En Brain Head And Neck Patologia Ultrasonido
Mortality caused by Ludwig angina was greater than 50 in the preantibiotic era1 The patient should be referred urgently to a head and neck specialist when Ludwig angina is diagnosed4 If the patient is sufficiently stable to allow radiologic investigations CT is useful to evaluate deep neck and mediastinal conditions5.
. ValenciaES Brought to you by. Ludwigs angina is a serious potentially life-threatening infection of the floor of the mouth. Infrequently Ludwigs angina has been documented to extend deeper into the soft tissues and progress to craniocervical necrotizing fasciitis 8.
Ludwig angina LA is a potentially lethal acute cellulitis of the floor of the mouth and subman dibular space. The most useful investigations in patients with suspected Ludwigs angina are clinical assessment a cervico-thoracic CT-scan to determine the extent of the lesions microbiological examination and panoramic radiography to detect possible dental focuses of infection. It is crucial for imaging modality to determine the airway patency of the patient 5.
Ludwigs angina 196542004 Definition. It usually results from infection in the lower molar area or from an infection following a penetrating injury to the MOUTH FLOOR. Ludwigs angina is a bacterial infection cellulitis that affects your neck and the floor of your mouth.
Llanes Rivada D. Care must be taken whilst imaging patients with floor of mouth swelling as they can obstruct the airway when lying flat on the CT scanner table. The first treatment is to make.
Evans Medicine Emergency Medicine Journal 2004 TLDR A review of the literature is undertaken to gain a better understanding of the disease and a summary of the key issues regarding this dreaded disease particularly the immediate management of it in the emergency department is presented. 83 PDF Ludwigs angina. It needs immediate treatment to get the infection under control and ensure your airway remains open.
CT Findings by. 70 of Ludwigs angina is odontogenic in origin CLINICAL FEATURES Mouth and throat pain Trismus limited mouth opening Hot potato voice Inability to swallow saliva and stridor suggest imminent airway compromise Fever tachycardia and progression to septic shock Bull neck appearance Tripod position and respiratory distress. Severe cellulitis of the submaxillary space with secondary involvement of the perimandibular spaces.
Ludwigs angina can be diagnosed with a CT scan or an magnetic resonance imaging by specificity and sensitivity. 1 This condition usually presents. It typically starts from a tooth infection abscessed tooth.
Diagnosis is established via radiographic imaging such as computed tomography CT. How Do You Treat Ludwigs Angina. Ludwigs angina is a serious and potentially life-threatening connective tissue infection found on the floor of the mouth and in the deep neck spaces.
Ludwig angina is primarily a clinical diagnosis but this case demonstrates findings that may be present on CT to support the diagnosis. Although LA is an uncommon entity it is a clinical emergency. Browse Posters Search result Poster ECR 2013 C-0520 POSTER SECTIONS Coverpage Learning objectives Background Imaging findings OR.
The patient in this case did not have clinically significant airway compromise and was treated with antibiotics. It is a type of phlegmonous infection of the soft tissue involving the floor of the mouth that rapidly extends bilaterally to the soft tissues of the oral cavity and neck. From MeSH Term Hierarchy.
Ludwig angina Ludwig angina is an infection of the submandibular space that most commonly arises from an infected Surgical management of necrotizing soft tissue infections Needle cricothyroidotomy with percutaneous transtracheal ventilation. CT features are in keeping with Ludwig angina cellulitis floor of mouth complicated with multiple sites of abscesses. Edema centered within the right submandibular space and base of the tongue with adjacent subcutaneous fat stranding has increased substantially with significant mass effect with effacement of the right side of the oropharynx.
Outline the typical presentation of a patient with Ludwigs angina. It is not contagious. Explain the interprofessional team strategies for improving care coordination and communication regarding the management of patients with Ludwigs angina.
Ironically Ludwig a German physician who described the condition died in 1865 from non specific neck inflammation which was probably Ludwig angina. CT Neck - 4 days later. ECR 2013 C-0520 Ludwigs Angina.
Conclusion Ludwigs angina is a type of cellulitis that produces airway occlusion and is rare progressive and potentially lethal. Treatment consists of ensuring adequate ventilation by securing the upper. Ludwigs angina is a serious infection that can spread rapidly.
Summarize the recommended treatment of Ludwigs angina. It rapidly spreads to infiltrate the soft tissues of the neck producing a suprahyoid brawny induration with posterior and superior displacement of the tongue. 1 article features images from this case Ludwig angina 15 public playlists include this case.
You will be admitted to the hospital for close monitoring imaging tests like a. Key findings are swelling of the floor of the mouth with loss of fat planes within the submandibular space and there can be focal fluid collections within the fascial spaces of the neck. This rare type of cellulitis can spread rapidly causing life-threatening swelling.
The two compartments affected are the sublingual space and the submylohyoid space. Ludwigs angina is an emergency and you should call 911 or get to the nearest emergency room as quickly as possible. This infection has resulted in elevation and posterior displacement of the tongue resulting in partial stenosis of airway at oral cavity and oropharynx.
1 article features images from this case. Ludwigs angina K.

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Brain Head And Neck Dental Extraction Bones Show Dental

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Brain Head And Neck Brain Anatomy Dental Extraction Ct Scan

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Brain Head And Neck Calculus Lymph Nodes Radiology

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Brain Head And Neck Lymph Nodes Mass Effect Tracheostomy

